eftec / routeone
Router service class for PHP
Installs: 1 293
Dependents: 2
Suggesters: 0
Security: 0
Stars: 29
Watchers: 4
Forks: 3
Open Issues: 1
Requires
- php: >=7.4
- ext-json: *
- eftec/clione: ^1.32
Requires (Dev)
- phpunit/phpunit: ^8.5.33
This package is auto-updated.
Last update: 2024-12-31 11:24:36 UTC
README
It reads the URL route and parses the values of path, so it could be interpreted manually or automatically in the fastest way possible (for example, to implement an MVC system).
Unlikely other libraries, this library does not have dependencies, and it is contained in a single class, so it is compatible with any PHP project, for example WordPress, Laravel, Drupal, a custom PHP project, etc.
This library is based in CoC Convention over Configuration. It reduces the boilerplate but it has fixed functionalities. This library does not allow to use custom "routes" but it covers practically all cases, so it increases the performance and usability while it sacrifices flexibility.
Table of contents
- RouteOne
- Table of contents
- Example:
- What it does?
- Getting started
- Using Paths
- Methods
- __construct($base='', $forcedType=null, $isModule=false)
- getQuery($key,$valueIfNotFound=null)
- setQuery($key,$value)
- fetch
- callObjectEx
- callFile($fileStructure='%s.php',$throwOnError=true)
- getHeader()
- getBody()
- getCurrentUrl($withoutFilename = true)
- getCurrentServer()
- setCurrentServer($serverName)
- getUrl($extraQuery = '',$includeQuery=false)
- url($module,$controller,$action,$id,$idparent)
- urlFront($module,$category,$subcategory,$subsubcategory,$id)
- alwaysWWW($https = false)
- alwaysHTTPS()
- alwaysNakedDomain($https = false)
- fields
- Whitelist
- CLI
- Changelog
Example:
Let's say we have the next URL http://somedomain.dom/Customer/Update/2 This library converts this URL into variables that could be process or directly calling a method.
route.php
$route=new RouteOne('http://www.somedomain.dom'); $route->addPath('api/{controller}/{action}/{id}'); $route->addPath('{controller}/{action}/{id}/{idparent}'); $route->fetchPath(); $this->callObjectEx('cocacola\controller\{controller}Controller');
controller\CustomerController.php class
namespace cocacola\controller\; class CustomerController { public function updateAction($id=null,$idparent=null,$event=null) { echo "We want to update the customer $id"; } }
What it does?
Let's say we do the next operation:
A user calls the next website http://somedomain.com/Customer/Insert, he wants to show a form to insert a customer
use \eftec\routeone\RouteOne; $route=new RouteOne('.',null,null); // Create the RouteOneClass $route->fetch(); // fetch all the input values (from the route, get, post and such). $route->callObject('somenamespace\\controller\\%sController'); // where it will call the class CustomerController*
or
use eftec\routeone\RouteOne; $route=new RouteOne('.',null,null); // Create the RouteOneClass $route->fetch(); // fetch all the input values (from the route, get, post and such). $route->callObjectEx('somenamespace\\controller\\{controller}Controller'); // where it will call the class CustomerController*
This code calls to the method InsertActionGet (GET), InsertActionPost (POST) or InsertAction (GET/POST) inside the class Customer
The method called is written as follows:
class Customer { public function insertAction($id="",$idparent="",$event="") { // here we do our operation. } }
What is $id, $idparent and $event?
id
Let's se we want to Update a Customer number 20, then we could call the next page
where 20 is the "$id" of the customer to edit (it could be a number of a string)
idparent
And what if we want to Update a Customer number 20 of the business APPL
Where APPL is the idparent
event
Now, let's say we click on some button, or we do some action. It could be captured by the field _event, and it is read by the argument $event. This variable could be sent via GET or POST.
Module
Note: Modules are obtained automatically if you use addPath() and fetchPath(), so you don't need to specify it. Now, let's say our system is modular, and we have several customers (internal customers, external, etc.)
$route=new RouteOne('.',null,true); // true indicates it is modular.
or
$route=new RouteOne('.',null,['Internal']); // or we determine the module automatically. In this case, every url that starts with Internal
then
$route->fetch(); $route->callObject('somenamespace\\%2s%\\controller\\%1sController');
http://somedomain.com/Internal/Customer/Update/20/APPL?_event=click
Then, the first ramification is the name of the module (Internal) and it calls the class somenamespace\Internal\controller\CustomerController
Getting started
Using the cli (recommended)
- Install the library
composer require eftec/routeone
- Execute the binary in the root folder
Linux:
vendor/bin/routeonecli -init (if the binary does not work, then chage the permission to execution)
Windows:
.\vendor\bin\routeonecli.bat -init
It will create the file .htaccess and the file route.php and route.php will have a default configuration.
- Edit the file route.php and change the next lines:
const BASEURL="http://localhost"; // Base url edit this value. const BASEWEBNS="eftec\\controller"; // Base namespace (web) edit this value const BASEAPINS="eftec\\api"; // Base namespace (api) edit this value
Later, you can add or edit the code in this file.
manual installation
1) Create a .htaccess file in the folder root (Apache)
<IfModule mod_rewrite.c>
<IfModule mod_negotiation.c>
Options -MultiViews -Indexes
</IfModule>
RewriteEngine On
DirectoryIndex route.php
# Handle Authorization Header
RewriteCond %{HTTP:Authorization} .
RewriteRule .* - [E=HTTP_AUTHORIZATION:%{HTTP:Authorization}]
# Redirect Trailing Slashes If Not A Folder...
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-d
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_URI} (.+)/$
RewriteRule ^ %1 [L,R=301]
# Send Requests To Front Controller...
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-d
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-f
RewriteRule ^ route.php?req=$1 [L,QSA]
</IfModule>
If your web host doesn't allow the FollowSymlinks option, try replacing it with Options +SymLinksIfOwnerMatch.
The important line is:
RewriteRule ^(.*)$ route.php?req=$1 [L,QSA] # The router to call.
Or configure nginx.conf (Nginx) Linux (not tested)
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
root /example.com/public;
add_header X-Frame-Options "SAMEORIGIN";
add_header X-XSS-Protection "1; mode=block";
add_header X-Content-Type-Options "nosniff";
index index.html index.htm index.php;
charset utf-8;
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ /router.php?req=$document_uri&$query_string;
}
location = /favicon.ico { access_log off; log_not_found off; }
location = /robots.txt { access_log off; log_not_found off; }
error_page 404 /index.php;
location ~ \.php$ {
fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php/php7.2-fpm.sock;
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $realpath_root$fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi_params;
}
location ~ /\.(?!well-known).* {
deny all;
}
}
The important line is:
try_files $uri $uri/ /router.php?req=$document_uri&$query_string;
Or configure nginx.conf (Nginx) Windows
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
root c:/www;
add_header X-Frame-Options "SAMEORIGIN";
add_header X-XSS-Protection "1; mode=block";
add_header X-Content-Type-Options "nosniff";
index index.html index.htm index.php;
charset utf-8;
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ /router.php?req=$document_uri&$query_string;
}
location = /favicon.ico { access_log off; log_not_found off; }
location = /robots.txt { access_log off; log_not_found off; }
error_page 404 /index.php;
location ~ \.php$ {
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi_params;
}
location ~ /\.(?!well-known).* {
deny all;
}
}
The important line is:
try_files $uri $uri/ /router.php?req=$document_uri&$query_string;
where router.php is the file that it will work as router. ?req=$1 is important because the system will read the route from "req"
// router.php $route=new RouteOne(); // Create the RouteOneClass $route->fetch(); // fetch all the input values (from the route, get, post and such). $route->callObject('somenamespace\\controller\\%sController'); // where it will call the class \somenamespace\controller\CustomerController
Note:
If you want to use an argument different as "req", then you can change it using the next code:
$route->argumentName='newargument';
Using Paths
Since 1.21, it is possible to use a custom path instead of a pre-defined path. It is the recommended way. The other method is still present.
clearPath()
Syntax:
clearPath()
It clears all the paths defined
addPath()
Syntax:
addPath($path, $name = null,callable $middleWare=null)
It adds a paths that could be evaluated using fetchPath()
Example:
$this->addPath('api/{controller}/{action}/{id:0}','apipath'); $this->addPath('/api/{controller}/{action}/{id:0}/','apipath'); // "/" at the beginner and end are trimmed. $this->addPath('{controller}/{action}/{id:0}','webpath'); $this->addPath('{controller:root}/{action}/{id:0}','webpath'); // root path using default $this->addPath('somepath','namepath', function(callable $next,$id=null,$idparent=null,$event=null) { echo "middleware\n"; $result=$next($id,$idparent,$event); // calling the controller echo "endmiddleware\n"; return $result; });
Note:
The first part of the path, before the "{" is used to determine which path will be used.
Example "path/{controller}" and "path/{controller}/{id}", the system will consider that are the same path
-
parameter string $path The path, example "aaa/{controller}/{action:default}/{id}"
Where default is the optional default value.- {controller}: The controller (class) to call
- {action}: The action (method) to call
- {verb}: The verb of the action (GET/POST,etc.)
- {type}: The type (value)
- {module}: The module (value)
- {id}: The id (value)
- {idparent}: The id parent (value)
- {category}: The category (value)
- {subcategory}: The subcategory (value)
- {subsubcategory}: The subsubcategory (value)
-
parameter string|null $name (optional), the name of the path
-
parameter callable|null $middleWare A callable function used for middleware.
The first argument of the function must be a callable method
The next arguments must be the arguments defined by callObjectEx
(id,idparent,event) -
The path could start with a static location but the rest of the path must be defined by variables (enclosed by {}) and separated by "/".
-
You can also set a default value for a path by writing ":" after the name of the variable: {name:defaultvalue}
-
The name could be obtained using $this->currentPath. If you add a name with the same name, then it is replaced.
-
If you don't set a name, then it uses an autonumeric.
-
The name is also returned when you call $this->fetchPath()
Example:
$this->addPath('{controller}/{id}/{idparent}'); $this->addPath('myapi/otherfolder/{controller}/{id}/{idparent}'); $this->addPath('{controller:defcontroller}/{action:defaction}/{id:1}/{idparent:2}'); // url: /dummy/10/20 =>(controller: dummy, id=10, idparent=20) // url: /myapi/otherfolder/dummy/10/20 =>(controller: dummy, id=10, idparent=20)
You can define different paths, however it only uses the first part of the path that matches some URL. 'path/somepath/{id}' will work 'path/{id}/other' will not work
fetchPath()
Syntax:
fetchPath()
It fetches the path previously defined by addPath, and it returns the name(or number) of the path. If not found, then it returns false
Example:
$route=new RouteOne('http://www.example.dom'); $route->addPath('{controller}/{id}/{idparent}','optionalname'); // if the url is : http://www.example.dom/customer/1/200 then it will return echo $route->fetchPath(); // optionalname echo $route->controller; // customer echo $route->id; // 1 echo $route->idparent; // 200
Methods
__construct($base='', $forcedType=null, $isModule=false)
- string $base base url
- string $forcedType=['api','ws','controller','front'][$i]
api then it expects a path as api/controller/action/id/idparent
ws then it expects a path as ws/controller/action/id/idparent
controller then it expects a path as controller/action/id/idparent
front then it expects a path as /category/subcategory/subsubcategory/id - bool $isModule if true then the route start reading a module name
false controller/action/id/idparent
true module/controller/action/id/idparent
array if the value is an array then the value is determined if the first part of the path is in the array.
Example ['modulefolder1','modulefolder2']
getQuery($key,$valueIfNotFound=null)
It gets a query value (URL).
Note: This query does not include the values "req","_event" and "_extra"
Example:
// http://localhost/..../?id=hi $id=$router->getQuery("id"); // hi $nf=$router->getQuery("something","not found"); // not found
setQuery($key,$value)
It sets a query value
Example:
$route->setQuery("id","hi"); $id=$router->getQuery("id"); // hi
fetch
Sintax:
fetchPath()
Fetch the values from the route, and the values are processed.
callObjectEx
Sintax
callObjectEx($classStructure, $throwOnError, $method, $methodGet, $methodPost,$arguments,$injectArguments)
It creates a new instance of an object (for example, a Controller object) and calls the method.
Note: It is an advanced version of this::callObject()
This method uses {} to replace values based in the next variables:
Example:
// controller example http://somedomain/Customer/Insert/23 $this->callObjectEx('cocacola\controller\{controller}Controller'); // it calls the method cocacola\controller\Customer::InsertAction(23,'',''); // front example: http://somedomain/product/coffee/nescafe/1 $this->callObjectEx('cocacola\controller\{category}Controller' // the class to call ,false // if error then it throw an error ,'{subcategory}' // the method to call (get, post or any other method) ,null // the method to call (method get) ,null // the method to call (method post) ,['subsubcategory','id'] // the arguments to call the method ,['arg1','arg2']); // arguments that will be passed to the constructor of the instance // it calls the method cocacola\controller\product::coffee('nescafe','1');
Call a method inside an object using the current route.
Example:
Router:
$databaseService=new SomeDatabaseService(); $route=new RouteOne(); $route->callObjectEx('cocacola\controller\{controller}Controller' // the class to call ,false // if error then it throw an error ,'{action}Action' // the method to call (get, post or any other method) ,'{action}Action{verb}' // the method to call (method get) ,'{action}Action{verb}' // the method to call (method post) ,['id', 'idparent', 'event'] // the arguments to call the method ,[$databaseService,$route]); // (optional)arguments that will be passed to the constructor of the instance
Controller:
namespace cocacola\controller; class CustomerController { protected $databaseService; protected $route; public function __construct($databaseService,$route) { // optional: injecting services $this->databaseService=$databaseService; $this->route=$route; } // any action GET or POST public function GreenAction($id="",$idparent="",$event="") { } // GET only action (optional) public function BlueActionGET($id="",$idparent="",$event="") { // **my code goes here.** } // POST only action (optional) public function YellowActionPOST($id="",$idparent="",$event="") { // **my code goes here.** } // GET only action (optional) public function RedActionGET($id="",$idparent="",$event="") { // **my code goes here.** } // any action GET or POST public function RedAction($id="",$idparent="",$event="") { // **my code goes here.** } }
Results:
callFile($fileStructure='%s.php',$throwOnError=true)
It calls (include) a php file using the current name of the controller
- $fileStructure The current name of the controller. "%s" is the name of the current controller. Example :/Customer/Insert -> calls the file Customer.php
- throwOnError if true then it throws an error. If false then it only returns the error message.
getHeader()
Syntax:
getHeader($key, $valueIfNotFound = null)
It gets the current header (if any). If the value is not found, then it returns $valueIfNotFound. Note, the $key is always converted to uppercase.
Example:
$token=$this->getHeader('token','TOKEN NOT FOUND');
getBody()
Syntax:
getBody($jsonDeserialize = false, $asAssociative = true)
It gets the body of a request.
Example:
$body=$this->getBody(); // '{"id"=>1,"name"=>john}' (as string) $body=$this->getBody(true); // stdClass {id=>1,name=>john} $body=$this->getBody(true,true); // ["id"=>1,"name"=>john]
getCurrentUrl($withoutFilename = true)
Returns the current base url without traling space, paremters or queries
Note: this function relies on $_SERVER['SERVER_NAME'], and it could be modified by the end-user
getCurrentServer()
It returns the current server without trailing slash.
$route->getCurrentServer(); // http://somedomain
setCurrentServer($serverName)
It sets the current server name. It is used by getCurrentUrl() and getCurrentServer().
Note: If $this->setCurrentServer() is not set, then it uses $_SERVER['SERVER_NAME'], and it could be modified
by the user.
$route->setCurrentServer('localhost'); $route->setCurrentServer('127.0.0.1'); $route->setCurrentServer('domain.dom');
getUrl($extraQuery = '',$includeQuery=false)
It gets the (full) url based in the information in the class.
$route->getUrl(); // http://somedomain/controller/action/id $route->getUrl('id=20'); // http://somedomain/controller/action/id?id=20 $route->getUrl('id=20',true); // http://somedomain/controller/action/id?id=20&field=20&field2=40
url($module,$controller,$action,$id,$idparent)
It builds an url based in custom values
$route->url(null,"Customer","Update",20); // Customer/Update/20
urlFront($module,$category,$subcategory,$subsubcategory,$id)
It builds an url (front) based in custom values
$route->url(null,"Daily","Milk",20); // Daily/Milk/20
alwaysWWW($https = false)
If the subdomain is empty or different to www, then it redirect to www.domain.com.
Note: It doesn't work with localhost, domain without TLD (netbios) or ip domains. It is on purpose.
Note: If this code needs to redirect, then it stops the execution of the code. Usually it must be called at the
top of the code
$route->alwaysWWW(); // if the domain is somedomain.dom/url, then it redirects to www.somedomain.dom/url $route->alwaysWWW(true); // if the domain is http: somedomain.dom/url, then it redirects to https: www.somedomain.dom/url
alwaysHTTPS()
If the page is loaded as http, then it redirects to https.
Note: It doesn't work with localhost, domain without TLD (netbios) or ip domains. It is on purpose.
Note: If this code needs to redirect, then it stops the execution of the code. Usually it must be called at
the top of the code
$route->alwaysHTTPS(); // http://somedomain.com ---> https://somedomain.com $route->alwaysHTTPS(); // http://localhost ---> // http://localhost $route->alwaysHTTPS(); // http://127.0.0.1 ---> // http://127.0.0.1 $route->alwaysHTTPS(); // http://mypc ---> // http://mypc
alwaysNakedDomain($https = false)
If the subdomain is www (example www.domain.dom) then it redirect to a naked domain domain.dom
Note: It doesn't work with localhost, domain without TLD (netbios) or ip domains. It is on purpose.
Note: If this code needs to redirect, then it stops the execution of the code. Usually,
it must be called at the top of the code
$route->alwaysNakedDomain(); // if the domain is www.somedomain.dom/url, then it redirects to somedomain.dom/url $route->alwaysNakedDomain(true); // if the domain is http: www.somedomain.dom/url, then it redirects to https: somedomain.dom/url
fields
Example:
$this->addPath('portal/web/{controller}/{action:list}'); $this->fetchPath(); var_dump($this-action); // it shows the current action or the default value "list" if none.
Whitelist
Whitelist input.
Whitelisting a method allows two operations:
- To whitelist an input, for example, only allowing "controllers" that they are inside a list.
- Also, it allows to define the case of an element.
For example:
// Example, value not in the whitelist: someweb.dom/customer/list $this->setWhiteList('controller',['Product','Client']); $this->fetch(); var_dump($this->controller); // null or the default value var_dump($this->notAllowed); // true (whitelist error) // Example, value in the whitelist but with the wrong case: someweb.dom/customer/list $this->setWhiteList('controller',['Customer']); $this->fetch(); var_dump($this->controller); // it shows "Customer" instead of "customer" var_dump($this->notAllowed); // false (not error with the validation of the whitelist) // reset whitelist for controllers $this->setWhiteList('controller',null);
CLI
Routeone contains a basic CLI to create and initialize the configuration. The binary routeonecli is located in the vendor/bin folder
- Execute routeonecli and it will show a menu with a simple option [router]
./vendor/bin/routeonecli
-
enter router and press enter.
- You can use the TAB key to autocomplete.
- You can use arrow-up and arrow-down to navigate in the options available
- If you write ?, it will show a simple help
- If you write ??, it will show a more technical help.
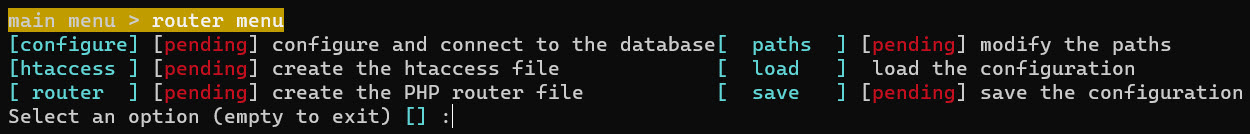
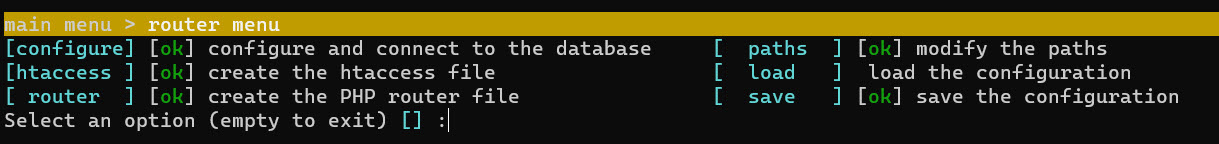
In the router menu, it will show the next screen:
Pending means that the operation is pending to do, or it requires something to configure.
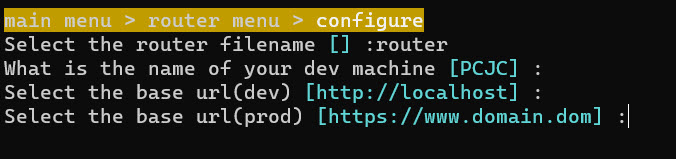
- enter configure
- And enters the router filename without extension.
- Then your developer machine. If you don't know, then press enter.
- Then your developer base url.
- And your production base url. If you don't have or don't know, then just use the default values
Once done, configure will be marked as "ok"
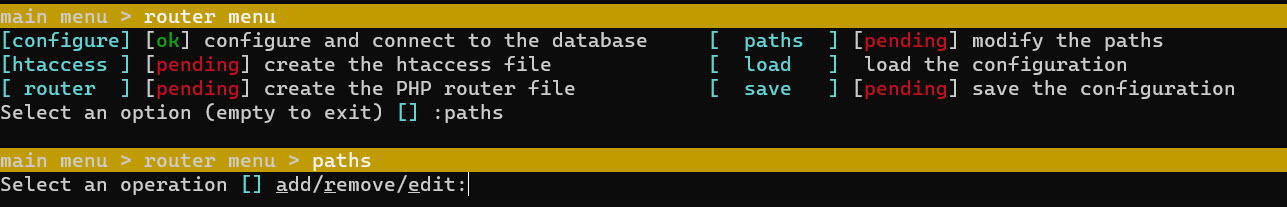
Now, lets configure the paths
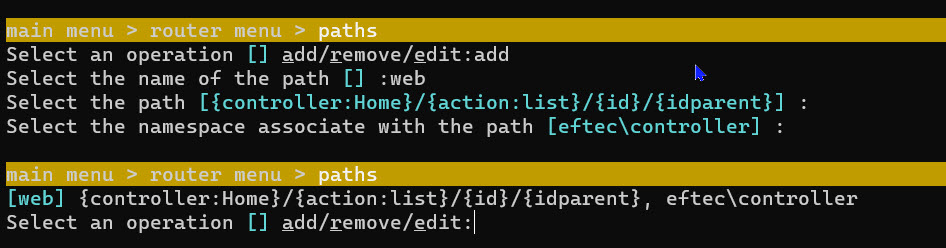
- Go to paths.
- And it will show the next menu, add, remove or edit.
- Enter add
- And enter the name of the path, example web.
- And the path (check path for see the syntax of the path)
- Finally, enter the name space associate with this path
- Once done, you have your first path. You can add more paths later.
- Press enter to return.
- Now, you can generate the htaccess file, the PHP router file, load the configuration, or save the configuration entered here.
- To exit press return and return.
Changelog
- 2024-12-31 1.34
- updated to PHP 8.4
- 2024-03-02 1.33
- Updating dependency to PHP 7.4. The extended support of PHP 7.2 ended 3 years ago.
- Added more type hinting in the code.
- 2024-01-22 1.32.1
- fixed a problem when the pattern doesn't have values, example "contact/"
- 2024-01-22 1.32
- unit test updated.
- now route file is always called index.php
- fetchPath() considers the field that is required and the field that is optional.
- 2024-01-09 1.31
- 2023-11-13 1.30.1
- fixed a bug with fetch() when the url fetched is null
- updated .htaccess, so it works better with different situations.
- 2023-05-08 1.30
- addPath() now allows to specify a middleware.
- 2023-04-02 1.29
- [RouteOneCli] updated
- new method instance() so we could get a singleton instance using RouteOne::instance();
- 2023-03-04 1.28
- Added static paths to addPath()
- callObjectEx() now allows any parameter. If the parameter is not a defined value, then it is obtained from the route.
- callObjectEx() now allows named parameter.
- callObjectEx() now allows to pass an instance and callable instead of the name of the class.
- callObjectEx() allows to filter by type of Path. By default, it does not filter value
- 2023-03-04 1.27.1
- Fix a small bug when addPath() add a path that starts with "/". Now, the value is trimmed.
- 2023-02-15 1.27
- Cleanup of the code and documentation. Deprecating old methods
- 2023-02-14 1.26.4
- some bug fixed
- 2023-01-27 1.26.2
- edited composer json (bin)
- 2023-01-27 1.26
- callObject() marked as deprecated, however you still could use it.
- arguments of function now uses type hinting/validation
- addPath() now throws an exception if the path is empty or null.
- new method redirect()
- new CLI.
- 2023-01-26 1.25
- some cleanups
- 2022-03-11 1.24
- [fix] fix many problems when the url is null.
- 2022-02-01 1.23
- [new] getRequest(), getPost(),getGet()
- 2022-01-27 1.22
- [new] callObjectEx allows adding arguments to the constructor.
- [new] clearPath()
- [new] addPath()
- [new] fetchPath()
- [new] getHeader()
- [new] getBody()
- 2021-04-24 1.20
- constructor Now it is possible to indicates the possible modules in the constructor.
- Many cleanups of the code.
- New field called $moduleList including its setter and getters (by default this value is null)
- If $moduleList is not null then it is used to determine if the URL is a module or not
- New field called $moduleStrategy assigned in the constructor and in the setter and getters (by default this value is 'none')
- 2021-02-26 1.19
- setWhiteList() now works with controller and category
- setWhiteList() also works to define the correct proper case of the elements.
- The method callObjectEx() allows to define the case.
- 2021-02-26 1.18
- new fields $verb (it gets the current verb, example GET, POST, etc.)
- new whitelist elements:
- $allowedVerbs The list of allowed verbs.
- $allowedFields The list of allowed fields used by callObjectEx()
- $allowedControllers The list of allowed controllers. If this list is set and the controller is not in the whitelist , then the controller is set as null
- The method callObjectEx() allows to use the verb. The verb is always ucfirst.
- Example $this->callObjectEx('cocacola\controller{controller}Controller','{action}Action{verb}');
- 2021-02-16 1.17
- removed all @ and replaced by isset(). Since this library is compatible with PHP 5.6, then it doesn't use "??" operators.
- setDefaultValues() trigger an error if it is called after fetch()
- 2021-02.11 1.16.1
- fixed a problem with "api" and "ws" that it doesn't read the controller in the right position.
- 2021-02-11 1.16
- Removed Travis.
- Lowered the requirement. Now, this library works in PHP 5.6 and higher (instead of PHP 7.0 and higher)
- Constructor has a new argument, it could fetch() the values
- alwaysHTTPS() has a new argument that it could return the full URL (if it requires redirect) or null
- alwaysWWW() has a new argument that it could return the full URL (if it requires redirect) or null
- alwaysNakedDomain() has a new argument that it could return the full URL (if it requires redirect) or null
- 2020-06-14 1.15
- Added default values in setDefaultValues().
- Method fetch() now it unset the value.
- Fixed Method url().
- 2020-06-07 1.14.2
- Bug fixed: Delete an echo (used for debug)
- 2020-06-07 1.14.1
- Solved a small bug. it keeps the compatibility.
- 2020-06-07 1.14
- added defcategory,defsubcategory and defsubsubcategory
- new method setIdentifyType()
- 2020-04-23 1.13
- Lots of cleanups.
- 2020-04-04 1.12
- added support for nginx.
- updated the documentation for .htaccess
- new method setCurrentServer()
- 2020-03-27 1.11
- added alwaysNakedDomain()
- 2020-03-27 1.10.1
- a small fix for alwaysHTTPS()
- 2020-03-27 1.10
- added method alwaysHTTPS() and alwaysWWW()
- 2020-02-15 1.9
- added new arguments to callObject()
- new method callObjectEx()
- 2020-02-03 1.8
- new method getNonRouteUrl()
- new method setExtra()
- new method isPostBack()
- new method setIsPostBack()
- Some fixes for getUrl()