overtrue / laravel-keycloak-guard
🔑 Simple Keycloak Guard for Laravel
Requires
- php: ^8.3
- ext-openssl: *
- firebase/php-jwt: ^6.3
Requires (Dev)
- laravel/pint: ^1.19
- nunomaduro/collision: ^8.5.0
- orchestra/testbench: ^9.9.0
- pestphp/pest: ^3.7.1
- phpunit/phpunit: ^11.5
This package is auto-updated.
Last update: 2025-01-13 08:27:29 UTC
README
Simple Keycloak Guard for Laravel
A fork of robsontenorio/laravel-keycloak-guard with additional features.
This package helps you authenticate users on a Laravel API based on JWT tokens generated from Keycloak Server.
Requirements
- Building an API with Laravel.
- Not using Laravel Passport for authentication, as Keycloak Server handles authentication.
- Frontend is a separate project.
- Frontend users authenticate directly on Keycloak Server to obtain a JWT token. This process is independent of the Laravel API.
- Frontend retains the JWT token from Keycloak Server.
- Frontend makes requests to the Laravel API with the JWT token.
Note: If your application does not meet these requirements, you might be looking for Socialite Providers Keycloak or Vizir Laravel Keycloak Web Guard.
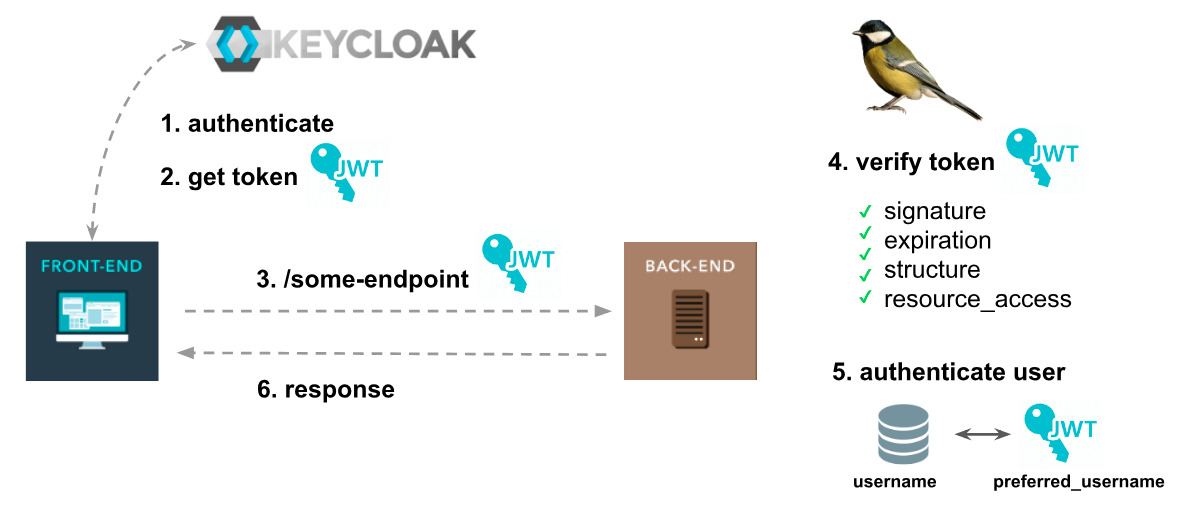
The flow
- The frontend user authenticates on Keycloak Server
- The frontend user obtains a JWT token.
- In another moment, the frontend user makes a request to some protected endpoint on a Laravel API, with that token.
- The Laravel API (through
Keycloak Guard) handle it.- Verify token signature.
- Verify token structure.
- Verify token expiration time.
- Verify if my API allows
resource accessfrom token.
- If everything is ok, then find the user on database and authenticate it on my API.
- Optionally, the user can be created / updated in the API users database.
- Return response
Installation
Require the package via Composer:
composer require overtrue/laravel-keycloak-guard
Example configuration (.env)
KEYCLOAK_REALM_PUBLIC_KEY=MIIBIj... # Get it on Keycloak admin web console. KEYCLOAK_LOAD_USER_FROM_DATABASE=false # You can opt to not load user from database, and use that one provided from JWT token. KEYCLOAK_APPEND_DECODED_TOKEN=true # Append the token info to user object. KEYCLOAK_ALLOWED_RESOURCES=my-api # The JWT token must contain this resource `my-api`. KEYCLOAK_LEEWAY=60 # Optional, but solve some weird issues with timestamps from JWT token.
Auth Guard
Update your config/auth.php to use the keycloak driver for API authentication.
'defaults' => [ 'guard' => 'api', // Set the default guard to 'api'. 'passwords' => 'users', ], 'guards' => [ 'api' => [ 'driver' => 'keycloak', // Use 'keycloak' as the driver for the 'api' guard. 'provider' => 'users', ], ],
Routes
Protect your API endpoints by applying the auth:api middleware in routes/api.php.
// public endpoints Route::get('/hello', function () { return ':)'; }); // protected endpoints Route::group(['middleware' => 'auth:api'], function () { Route::get('/protected-endpoint', 'SecretController@index'); // ... });
Any routes within the auth:api middleware group will require a valid JWT token issued by Keycloak Server for access.
Configuration
Keycloak Guard
⚠️ When editing .env, ensure all strings are trimmed to avoid parsing issues.
php artisan vendor:publish --provider="KeycloakGuard\KeycloakGuardServiceProvider"
Configuration Options
Below are the configuration options available for Keycloak Guard:
realm_public_key
- Type:
string - Required: Yes
- Description: The public key of your Keycloak realm. Obtain it from the Keycloak admin console under “Realm Settings” > “Keys” > “Public Key”.
token_encryption_algorithm
- Type:
string - Default:
RS256 - Description: The JWT token encryption algorithm used by Keycloak.
load_user_from_database
- Type:
boolean - Default:
true - Description: Determines whether to load the user from the database. Set to false if you do not have a
userstable or prefer not to load users from the database, the user object will be created from\Keycloak\Userclass.
user_provider_custom_retrieve_method
- Type:
string|null - Default:
null - Description: Specifies a custom method in your user provider to retrieve users based on the decoded token. Requires
load_user_from_databaseto betrue.
user_provider_credential
- Type:
string - Default:
username - Description: The field in the
userstable used to identify the user (e.g.,username,email).
token_principal_attribute
- Type:
string - Default:
preferred_username - Description: The attribute in the JWT token that contains the user identifier.
append_decoded_token
- Type:
boolean - Default:
false - Description: If set to
true, appends the full decoded JWT token to the authenticated user object ($user->token).
allowed_resources
- Type:
string - Required: Yes
- Description: A comma-separated list of resources that the JWT token must contain for access.
ignore_resources_validation
- Type:
boolean - Default:
false - Description: Disables resource validation, ignoring the allowed_resources configuration.
leeway
- Type:
integer - Default:
0 - Description: Adds a leeway (in seconds) to account for clock skew between servers. Useful for resolving timestamp-related token issues.
input_key
- Type:
string|null - Default:
null - Description: If set, the guard will look for a token in this custom request parameter in addition to the Bearer token.
Example Usage:
// keycloak.php 'input_key' => 'api_token'
With this configuration, if there is no Bearer token in the request, the guard will use the api_token request parameter:
- GET request:
/foo/secret?api_token=xxxxx - POST request:
/foo/secretwith["api_token" => "xxxxx"]in the body.
API
Simple Keycloak Guard implements Illuminate\Contracts\Auth\Guard. So, all Laravel default methods will be available.
Default Laravel methods
check()guest()user()id()validate()setUser()
Keycloak Guard methods
Token
token()
Returns full decoded JWT token from authenticated user.
$token = Auth::token() // or Auth::user()->token()
Role
hasRole('some-resource', 'some-role')
Check if authenticated user has a role on resource_access
// Example decoded payload 'resource_access' => [ 'myapp-backend' => [ 'roles' => [ 'myapp-backend-role1', 'myapp-backend-role2' ] ], 'myapp-frontend' => [ 'roles' => [ 'myapp-frontend-role1', 'myapp-frontend-role2' ] ] ]
Auth::hasRole('myapp-backend', 'myapp-backend-role1') // true Auth::hasRole('myapp-frontend', 'myapp-frontend-role1') // true Auth::hasRole('myapp-backend', 'myapp-frontend-role1') // false
hasAnyRole('some-resource', ['some-role1', 'some-role2'])
Check if the authenticated user has any of the roles in resource_access
Auth::hasAnyRole('myapp-backend', ['myapp-backend-role1', 'myapp-backend-role3']) // true Auth::hasAnyRole('myapp-frontend', ['myapp-frontend-role1', 'myapp-frontend-role3']) // true Auth::hasAnyRole('myapp-backend', ['myapp-frontend-role1', 'myapp-frontend-role2']) // false
Scope
Example decoded payload:
{
"scope": "scope-a scope-b scope-c",
}
scopes()
Get all user scopes
array:3 [ 0 => "scope-a" 1 => "scope-b" 2 => "scope-c" ]
hasScope('some-scope')
Check if authenticated user has a scope
Auth::hasScope('scope-a') // true Auth::hasScope('scope-d') // false
hasAnyScope(['scope-a', 'scope-c'])
Check if the authenticated user has any of the scopes
Auth::hasAnyScope(['scope-a', 'scope-c']) // true Auth::hasAnyScope(['scope-a', 'scope-d']) // true Auth::hasAnyScope(['scope-f', 'scope-k']) // false
Acting as a Keycloak user in tests
As an equivalent feature like $this->actingAs($user) in Laravel, with this package you can use KeycloakGuard\ActingAsKeycloakUser trait in your test class and then use actingAsKeycloakUser() method to act as a user and somehow skip the Keycloak auth:
use KeycloakGuard\ActingAsKeycloakUser; public test_a_protected_route() { $this->actingAsKeycloakUser() ->getJson('/api/somewhere') ->assertOk(); }
If you are not using keycloak.load_user_from_database option, set keycloak.preferred_username with a valid preferred_username for tests.
You can also specify exact expectations for the token payload by passing the payload array in the second argument:
use KeycloakGuard\ActingAsKeycloakUser; public test_a_protected_route() { $this->actingAsKeycloakUser($user, [ 'aud' => 'account', 'exp' => 1715926026, 'iss' => 'https://localhost:8443/realms/master' ])->getJson('/api/somewhere') ->assertOk(); }
$user argument receives a string identifier or an Eloquent model, identifier of which is expected to be the property referred in user_provider_credential config.
Whatever you pass in the payload will override default claims,
which includes aud, iat, exp, iss, azp, resource_access and either sub or preferred_username,
depending on token_principal_attribute config.
Alternatively, payload can be provided in a class property, so it can be reused across multiple tests:
use KeycloakGuard\ActingAsKeycloakUser; protected $tokenPayload = [ 'aud' => 'account', 'exp' => 1715926026, 'iss' => 'https://localhost:8443/realms/master' ]; public test_a_protected_route() { $payload = [ 'exp' => 1715914352 ]; $this->actingAsKeycloakUser($user, $payload) ->getJson('/api/somewhere') ->assertOk(); }
Priority is given to the claims in passed as an argument, so they will override ones in the class property.
$user argument has the highest priority over the claim referred in token_principal_attribute config.
Contribute
Contributions are welcome! To contribute to this project, please follow these steps:
-
Fork the Repository
-
Click the "Fork" button at the top right of the repository page to create your own fork.
-
Clone Your Fork
git clone https://github.com/yourusername/your-forked-package.git
cd your-forked-package
- Create a New Branch
git checkout -b feature/your-feature-name
- Make Your Changes
- Implement your feature or bug fix.
- Ensure your code follows the project’s coding standards.
- Run Tests
composer install
composer test
- Commit Your Changes
git commit -m "Add feature: your feature description"
- Push to Your Fork
git push origin feature/your-feature-name
- Create a Pull Request
- Navigate to your forked repository on GitHub.
- Click the “Compare & pull request” button.
- Provide a clear description of your changes and submit the Pull Request.
For more detailed guidelines, please refer to the CONTRIBUTING.md file.
Credits
This project is a fork of the original work by Robson Tenório. Special thanks to Robson for creating and maintaining the original codebase, which served as the foundation for this project. Your contributions and dedication to open-source development are greatly appreciated!
Contact
You can reach me on Twitter or create an issue.
License
MIT